sampling method quantitative|quantitative sampling techniques pdf : manufacturer In a non-probability sample, individuals are selected based on non-random criteria, and not every individual has a chance of being included. This type of sample is easier and cheaper to access, but it has a higher risk of sampling bias. That means the inferences you . See more WEBJully.poca (insta) Jully.pca (tiktok)Twitch (Jullypoca)
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBInstagram
First, you need to understand the difference between a population and a sample, and identify the target population of your research. 1. The populationis the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about. 2. The sampleis the specific group of individuals that you will collect data from. The population can be . See moreProbability sampling means that every member of the population has a chance of being selected. It is mainly used in quantitative research. If you want to produce results that . See more
In a non-probability sample, individuals are selected based on non-random criteria, and not every individual has a chance of being included. This type of sample is easier and cheaper to access, but it has a higher risk of sampling bias. That means the inferences you . See moreIf you want to know more about statistics, methodology, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples. See more
In quantitative research, collecting data from an entire population of a study is impractical in many instances. It squanders resources like time and money which can be .Researchers focus on the specific techniques that will yield highly representative samples (i.e., samples that are very much like the population). Quantitative researchers tend to use a type of . Sampling methods refer to the techniques used to select a subset of individuals or units from a larger population for the purpose of conducting statistical analysis or research. This article reviews probability and non-probability sampling methods, lists and defines specific sampling techniques, and provides pros and cons for consideration. In .
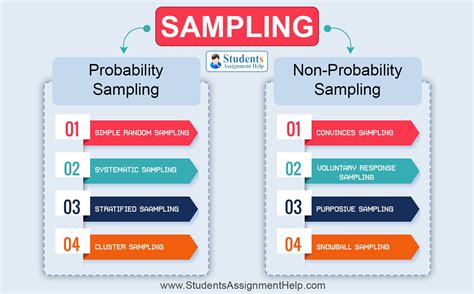
There are two types of sampling methods: Probability sampling involves random selection, allowing you to make strong statistical inferences about the whole group. It minimises the risk of selection bias. Non-probability .
In quantitative research, collecting data from an entire population of a study is impractical in many instances. It squanders resources like time and money which can be minimized by choosing .
Probability sampling is a sampling method that involves randomly selecting a sample, or a part of the population that you want to research. Probability sampling Sampling methods in psychology refer to strategies used to select a subset of individuals (a sample) from a larger population, to study and draw inferences about the entire population. Common methods include . Probability sampling. Unlike nonprobability sampling, probability sampling refers to sampling techniques for which a person’s likelihood of being selected from the sampling frame is known. You might ask yourself why we .
When to use simple random sampling. Simple random sampling is used to make statistical inferences about a population. It helps ensure high internal validity: randomization is the best method to reduce the impact of potential confounding variables.. In addition, with a large enough sample size, a simple random sample has high external validity: it represents the . Probability sampling. In quantitative research, it is important that your sample is representative of your target population. This allows you to make strong statistical inferences based on the collected data. . as it will help you decide if this is the right sampling method for your research design. Advantages of probability sampling; When to use purposive sampling. Purposive sampling is best used when you want to focus in depth on relatively small samples.Perhaps you would like to access a particular subset of the population that shares certain characteristics, or you are researching issues likely to have unique cases.. The main goal of purposive sampling is to identify the cases, individuals, .There are two broad classes of sampling in quantitative research: Probability and nonprobability sampling. Probability sampling: . Common Data Collection Methods in Quantitative Research. There are various methods that researchers use to collect data for their studies. For nurse researchers, existing records are an important data source.
We could choose a sampling method based on whether we want to account for sampling bias; a random sampling method is often preferred over a non-random method for this reason. Random sampling examples include: simple, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling. Non-random sampling methods are liable to bias, and common examples include . Non-probability sampling methods are those in which elements are chosen through non-random methods for inclusion into the research study and include convenience sampling, purposive sampling, and . Sampling in quantitative research. July 2008; Paediatric Care 20(5):37 . were chosen using a random sampling method. Such a sampling approach aims to provide an unbiased representation of the .
You might remember studying sampling in a quantitative research course. Sampling is important here too, but it works a bit differently. Unlike quantitative research, qualitative research involves nonprobability sampling. This chapter explains why this is so and what qualities instead make a good sample for qualitative research. Introduction. Sampling is a critical, often overlooked aspect of the research process. The importance of sampling extends to the ability to draw accurate inferences, and it is an integral part of qualitative guidelines across research methods. Sampling Methods | Types, Techniques, & Examples. Published on 3 May 2022 by Shona McCombes.Revised on 10 October 2022. When you conduct research about a group of people, it’s rarely possible to collect data from every person in that group. Instead, you select a .
Quantitative researchers are often interested in being able to make generalizations about groups larger than their study samples. While there are certainly instances when quantitative researchers rely on nonprobability samples (e.g., when doing exploratory or evaluation research), quantitative researchers tend to rely on probability sampling techniques.Purposive sampling (also known as judgment, selective or subjective sampling) is a sampling technique in which researcher relies on his or her own judgment when choosing members of population to participate in the study. Purposive .
types of quantitative sampling methods
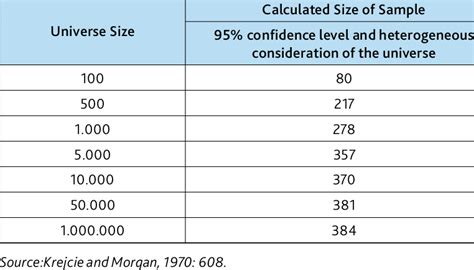
sampling size for quantitative research
Quantitative research methods. You can use quantitative research methods for descriptive, correlational or experimental research. In descriptive research, you simply seek an overall summary of your study variables.; In correlational research, you investigate relationships between your study variables.; In experimental research, you systematically examine whether .
The research utilized a quantitative-correlation design involving 1,494 respondents selected through simple random sampling. . The sampling method is significant to strengthen the . Non-probability Sampling Methods. Another class of sampling methods is known as non-probability sampling methods because not every member in a population has an equal probability of being selected to be in the sample. This type of sampling method is sometimes used because it’s much cheaper and more convenient compared to probability .
sampling methods research methodology how to choose a technique for
What Is Snowball Sampling? | Definition & Examples. Published on August 17, 2022 by Kassiani Nikolopoulou.Revised on June 22, 2023. Snowball sampling is a non-probability sampling method where new units are recruited by other units to form part of the sample.Snowball sampling can be a useful way to conduct research about people with .
quantitative sampling techniques pdf
There are two main sampling methods for quantitative research: Probability and Non-probability sampling.. Probability sampling. A theory of probability is used to filter individuals from a population and create samples in probability sampling.Participants of a sample are chosen by random selection processes. Quantitative researchers are often interested in being able to make generalizations about groups larger than their study samples. While there are certainly instances when quantitative researchers rely on nonprobability samples (e.g., when doing exploratory or evaluation research), quantitative researchers tend to rely on probability sampling techniques. When you use the sampling method, the whole population being studied is called the sampling frame. The sample you choose should represent your target market, or the sampling frame, well enough to do one of the following: . Probability sampling is used in quantitative research, so it provides data on the survey topic in terms of numbers . This sampling technique is also known as judgmental sampling or selective sampling, and it is often used when the population being studied is too small, too difficult to access, or too heterogeneous to use probability sampling methods. Purposive Sampling Methods. Purposive Sampling Methods are as follows: Expert sampling: In expert sampling .
What Is Non-Probability Sampling? | Types & Examples. Published on July 20, 2022 by Kassiani Nikolopoulou.Revised on June 22, 2023. Non-probability sampling is a sampling method that uses non-random criteria like the availability, geographical proximity, or expert knowledge of the individuals you want to research in order to answer a research question.
quantitative sampling methods pdf
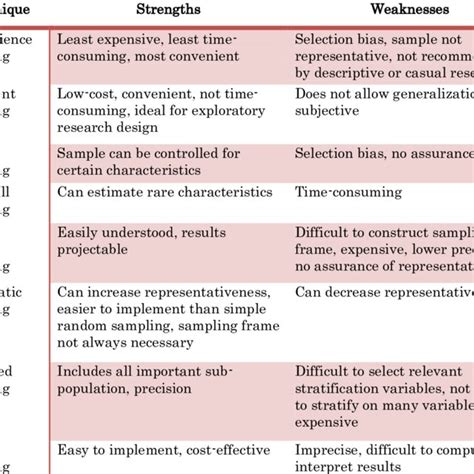
Systematic sampling is a probability sampling method in which researchers select members of the population at a regular interval (or k) determined in advance. If the population order is random or random-like (e.g., alphabetical), then this method will give you a representative sample that can be used to draw conclusions about your population of . Stratified Random Sampling Methods. There are two Stratified Random Sampling Methods: Proportional Stratified Random Sampling: In this method, the sample size for each stratum is proportional to the size of that stratum in the population. For example, if a population has three strata with sizes of 1000, 2000, and 3000, and a total sample size . What Is Convenience Sampling? | Definition & Examples. Published on August 9, 2022 by Kassiani Nikolopoulou.Revised on June 22, 2023. Convenience sampling is a non-probability sampling method where units are selected for inclusion in the sample because they are the easiest for the researcher to access.. This can be due to geographical proximity, .
Fortune Ox by PG Soft is a 5 reel, 3 row slot with respins, bonus games & 10x multiplier reels! Become a Master of the Bull in this slot at Stake.com.
sampling method quantitative|quantitative sampling techniques pdf